
Understanding the Role of a Site Reliability Engineer (SRE)
In today’s digital-first world, businesses rely on highly available, scalable, and resilient systems to maintain seamless operations. A single instance of downtime can lead to significant financial losses, customer dissatisfaction, and operational inefficiencies. This is where the role of a Site Reliability Engineer (SRE) becomes essential.

What is a Site Reliability Engineer (SRE)?
A Site Reliability Engineer (SRE) is a specialized IT professional who blends software engineering with IT operations to create scalable and highly reliable systems. The SRE role was pioneered to bridge the gap between development and operations by ensuring that software applications remain available, efficient, and secure.
SREs focus on automating system reliability, optimizing performance, and preventing failures through proactive monitoring and incident management. Their expertise allows organizations to achieve a balance between speed of software development and system stability, ultimately enhancing user experience and business continuity.
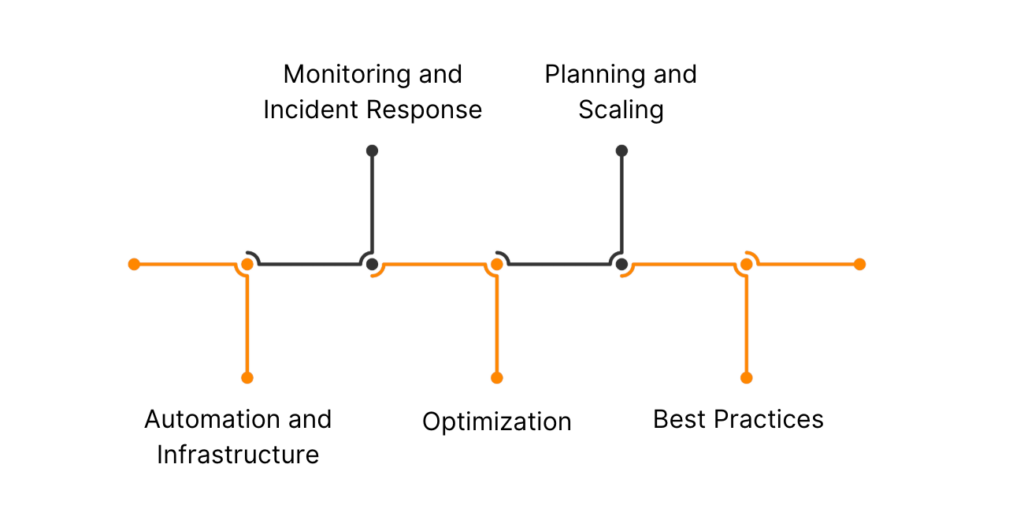
Key Responsibilities of an SRE
- Automation and Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
SREs leverage automation tools to reduce manual interventions in system administration tasks. From deploying applications to managing cloud infrastructure, automation ensures efficiency, repeatability, and minimal human error. - System Monitoring and Incident Response
One of the primary responsibilities of an SRE is setting up monitoring systems to track performance metrics and identify potential issues before they impact users. They also develop incident response protocols to minimize downtime in case of failures. - Performance Optimization
SREs continuously assess system performance, identifying bottlenecks and optimizing applications to improve speed, scalability, and resource utilization. - Capacity Planning and Scaling
As businesses grow, their IT infrastructure must scale accordingly. SREs analyze system demands and plan for future growth by optimizing cloud resources, databases, and network configurations. - Reliability Engineering Best Practices
SREs implement strategies such as error budgets, service level objectives (SLOs), and postmortems to maintain high system reliability and learn from past incidents.
Why SREs are Essential for Modern Businesses
The integration of SRE principles leads to enhanced operational efficiency, reduced downtime, and improved collaboration between development and operations teams. By focusing on automation, monitoring, and performance optimization, SREs play a crucial role in ensuring that businesses maintain high availability and reliability in an increasingly digital landscape.
Conclusion
The role of a Site Reliability Engineer has become increasingly important in today’s technology-driven world. By combining software engineering principles with operational excellence, SREs help businesses maintain stable, high-performing systems. Organizations looking to enhance their system reliability and optimize IT operations should consider adopting SRE best practices as a strategic approach to achieving long-term success.
To conclude, Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) principles closely mirror traditional reliability engineering practices by emphasizing both proactive system design and reactive problem-solving. Root cause analysis plays a central role in SRE, as teams focus on “triage and mitigate first—investigate root causes later,” minimizing service disruptions and uncovering opportunities for long-term improvements. By integrating root cause analysis techniques into day-to-day SRE workflows, organizations gain deeper insights into production incidents, leading to more robust preventative measures and overall system-wide reliability.
For a practical perspective on how SREs implement these methods, listen to our Reliability 4.0 Podcast episode featuring Google’s SRE Manager, Yuri Grinshteyn. Yuri discusses how his team applies root cause analysis post-incident, uses data-driven triage to reduce time-to-mitigation, and aligns these efforts with the needs of enterprise customers – offering a real-world example of how SRE best practices strengthen an organization’s overall reliability strategy.
Recent Posts
Measuring Training Efficacy: KPIs for Your Global RCA Education Strategy
7 Steps to RCA Success: What High-Performing Teams Do After the Investigation Ends
How to Improve Your RCA Program: A Practical Guide for Reliability Leaders
The 2026 Reliability Cost Curve: How World-Class Teams Bend It Downward
Root Cause Analysis Software
Our RCA software mobilizes your team to complete standardized RCA’s while giving you the enterprise-wide data you need to increase asset performance and keep your team safe.
Root Cause Analysis Training

