
Richmond Water Crisis Exposes Infrastructure Vulnerabilities: Why RCA Is Key to Long-Term Solutions

What Happened in Richmond?
In the early hours of May 27, 2025, a large portion of Richmond, Virginia woke up to a frustrating and unexpected problem—dry taps and low water pressure. What began as overnight maintenance work quickly led to a city-wide boil water advisory, with officials urging residents not to drink or cook with tap water unless it was first brought to a rolling boil for at least one minute.
City officials linked the disruption to scheduled work at the Ginter Park water tank. However, further investigation reveals the incident may have begun even earlier than the city acknowledged. According to internal communications, Henrico officials became aware of issues at Richmond’s water treatment plant at approximately 12:27 a.m. Tuesday, when the plant superintendent reported that a majority of the city’s filters had been clogged by excessive sediment in the James River.
Despite this, Richmond continued to report that the water was safe to drink well into the morning. As of 9:00 a.m., no boil advisory had been issued—only for the city to reverse course hours later. One press release even claimed that “the water plant continued to produce enough water to maintain safe water pressure levels to avoid a boil water advisory,” a claim that now appears to be in tension with the early warnings shared with neighboring counties.
As of May 29, the advisory was still in place for some neighborhoods pending test results.
The Timeline Breakdown
May 27, 12:27 AM: Henrico officials receive a report from Richmond’s water plant superintendent that most filters are clogged due to sediment from the James River.
May 27, 12:30 AM: Richmond’s Department of Public Utilities begins maintenance work at the Ginter Park water tank.
May 27, Morning: Despite reports of filter clogs and low pressure, Richmond states that water remains safe to drink.
May 27, Midday: Boil water advisory is issued across affected neighborhoods.
May 28: Water pressure returns to most areas, but the advisory remains pending testing for contaminants.
May 29: Boil advisory still active in parts of the city, including Northside.
Recurring Problem?
The water outage and boil water advisory in May, 2025, was preceded by an even more severe water outage in January, 2025. The January outage had already led to a public outcry and a detailed investigation summarized in a major report released by the Virginia Department of Health, Office of Drinking Water on April 8, 2025: Comprehensive Waterworks Evaluation and Cost Estimate
Where Did It Go Wrong?
Solving this kind of issue takes more than a quick technical fix. Cities need to dig deeper—using structured root cause analysis (RCA) to identify the real issues that enable these failures to occur in the first place.
At Reliability Center Inc., we used the PROACT® RCA methodology and our EasyRCA software to analyze the event. While we didn’t have direct access to the facility or complete operational records, we built a logic tree to explore what a thorough RCA could uncover—and the kind of corrective actions that would follow.
These root causes and corrective actions are based on information that was publicly available and are not intended to be 100% conclusive.
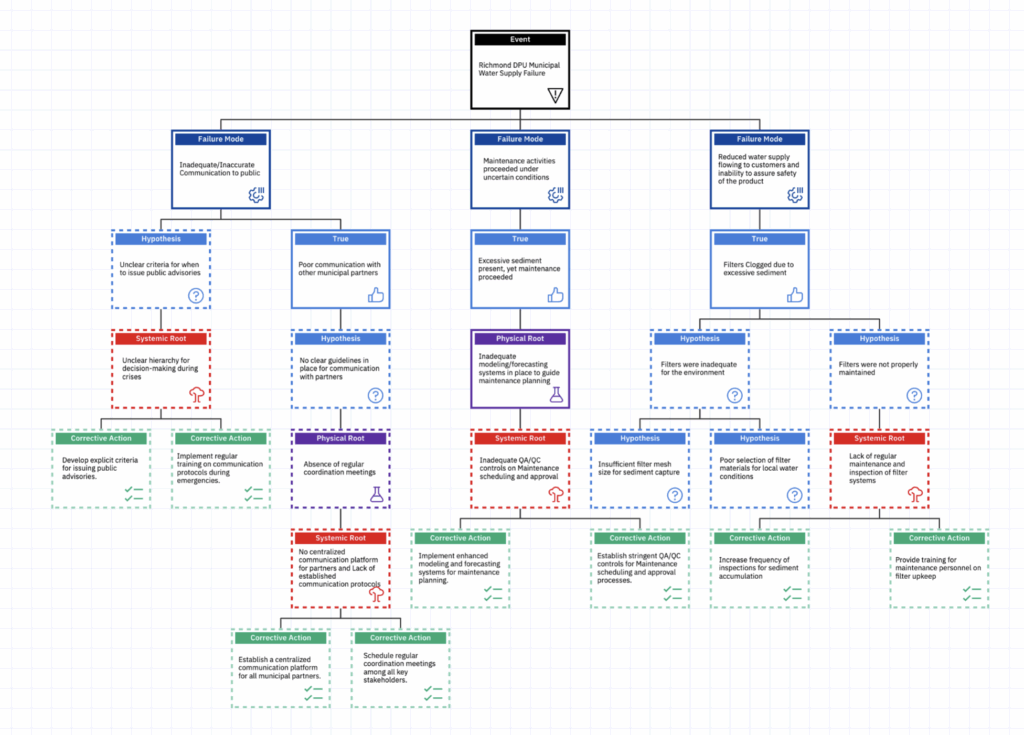
Our analysis identified three primary failure modes:
- Inadequate/Inaccurate Communication to the Public
- Maintenance Activities Proceeded Under Uncertain Conditions
- Reduced Water Supply and Inability to Assure Safety Due to Clogged Filters
Each of these led us beyond the surface to deeper systemic root causes, including:
- Lack of clear criteria and decision-making authority for public advisories
- No centralized communication platform for emergency coordination
- Poor sediment modeling and QA/QC processes
- Inadequate filter maintenance and mismatch between filter design and local conditions
With EasyRCA, we were able to map this out clearly and identify targeted, systemic corrective actions—like improved training, centralized communication protocols, sediment forecasting, and proactive maintenance systems.
Lessons for City Leaders and Utilities
- You Can’t Fix What You Don’t Understand
Band-aid fixes and PR statements don’t prevent repeat failures. Cities must adopt structured methodologies like PROACT® to uncover the real causes of failure—and take action to prevent recurrence. - Communication Isn’t Just External
Our RCA showed major breakdowns between departments and neighboring municipalities. Emergency communication protocols must be clear, practiced, and designed for coordination across agencies. - You Must Think Systemically
What appears to be a technical issue (e.g., clogged filters) often has deeper human and systemic causes—like poor planning, lack of QA/QC, or inadequate forecasting. RCA helps you see the full picture. - Use the Right Tools
Effective RCA requires more than whiteboards and guesswork. Tools like EasyRCA guide your team through a structured, repeatable process—from hypothesis generation to root cause validation—so nothing gets missed and decisions are data-driven. They also speed up the analysis, making it easier to respond before small issues become public crises. - RCA Is a Process, Not a Blame Game
PROACT® provides a clear framework to explore failures objectively and productively. The goal isn’t to assign fault—it’s to build better systems that don’t break under pressure. - Invest in People and Process Before Crisis Hits
If your team isn’t trained in structured RCA or lacks clear maintenance, QA, and emergency procedures, the time to act is before the next failure—not after.
Start Solving the Right Problems
At Reliability Center Inc., we help teams uncover and address the true root causes of complex failures—before they escalate into public crises. Whether you manage a public utility, city infrastructure, or a private facility, our PROACT® RCA training and EasyRCA software can give your team the clarity, confidence, and tools they need to solve problems at the root.
Want to see how it works?
👉 Explore PROACT RCA Training Options
Let’s stop guessing—and start solving.
Recent Posts
AI in Root Cause Analysis: How Emerging Tools Are Changing Reliability
AI and Site Reliability Engineers: Lessons from the Field.
Smarter, Faster, Deeper: How AI Is Transforming Root Cause Analysis in Software and Beyond
North America’s Looming Power Shortfall: A Root Cause Analysis for the Grid—and Beyond
Root Cause Analysis Software
Our RCA software mobilizes your team to complete standardized RCA’s while giving you the enterprise-wide data you need to increase asset performance and keep your team safe.
Root Cause Analysis Training

