
How To Conduct Incident Analysis?
- The Importance of Incident Analysis
- Key Objectives of Incident Analysis
- How to Conduct Incident Analysis?
- Challenges in Incident Analysis
- The Role of Technology in Incident Analysis
- Implementing a Successful Incident Analysis Process
- Case Studies and Real-World Examples
- The Integration of Incident Analysis Across Departments
- Conclusion: The Path Forward with Incident Analysis
With over two decades in business – spanning strategy consulting, tech startups, and executive leadership – I am committed to helping your organization thrive.
At Reliability, we’re on a mission to help enhance strategic decision-making and operational excellence through the power of Root Cause Analysis, and I hope this article will be helpful!
Our goal is to help you better understand root cause analysis by offering insights and practical tips based on years of experience. Whether you’re new to doing RCAs or a seasoned pro, we trust this will be useful in your journey towards working hard and working smart.
———————
Incident analysis is a systematic process used by organizations to understand the factors that led to an unexpected event, whether it resulted in actual harm or merely had the potential to do so. This article will cover what incident analysis entails and how it can be effectively conducted to foster continuous improvement and ensure compliance with industry standards.
The Importance of Incident Analysis
At its core, incident analysis is about understanding the “why” and “how” of adverse events to prevent future occurrences. This process helps in identifying the immediate causes of an incident and also uncovers underlying systemic issues that could lead to similar events. By thoroughly analyzing incidents, organizations can develop more resilient systems and processes, enhance employee training, and implement better safety measures, ultimately leading to a safer and more efficient workplace.
Key Objectives of Incident Analysis
- Identifying Root Causes: Unlike surface-level examination, incident analysis aims to dig deeper to find the root causes of an incident. This involves looking beyond obvious mistakes and understanding systemic issues.
- Improving Processes: Insights gained from incident analysis are used to refine organizational processes and prevent the recurrence of similar incidents.
- Enhancing Safety Culture: Regular incident analysis contributes to a culture of safety where learning and continuous improvement are valued over blame and punishment.
How to Conduct Incident Analysis?
Conducting effective incident analysis is a structured process that involves several key steps. Each step is designed to help organizations extract actionable insights from incidents, which can be used to fortify their operational practices.

Step 1: Incident Identification
The first step in incident analysis is recognizing and recording an incident. This involves determining whether an event qualifies as an incident based on predefined criteria within the organization. All relevant details such as the time, location, and initial observations should be meticulously documented.
Step 2: Data Collection
Once an incident is identified, gather all possible data related to the event. This includes witness statements, physical evidence, digital data logs, and relevant environmental conditions. Comprehensive data collection ensures that the analysis is based on robust information, reducing the risk of oversight or bias.
Step 3: Data Analysis
With all the data in hand, the next step is to analyze it to identify trends, patterns, and anomalies. Techniques such as causal analysis, fault tree analysis, or the “Five Whys” method are commonly used to trace the sequence of events that led to the incident. This phase is critical in moving beyond symptoms to understanding the underlying causes.
Step 4: Developing Corrective Actions
Based on the findings from the data analysis, develop corrective actions that are specific, measurable, and achievable. These actions should directly address the root causes identified in the previous step. It’s essential that these measures are not merely reactive but are designed to enhance systems and processes to prevent future incidents.
Step 5: Implementation of Corrective Actions
Implementing corrective actions involves planning, resource allocation, and change management. It’s important to communicate clearly with all stakeholders about the changes being made, why they are necessary, and how they will be implemented. Adequate training and support should be provided to ensure that the changes are effectively integrated into daily operations.
Step 6: Monitoring and Review
The final step in incident analysis is monitoring the effectiveness of the corrective actions. This involves regular reviews and audits to ensure that the actions are functioning as intended and are contributing to safer, more efficient operations. Feedback mechanisms should also be established to continually refine and improve the incident analysis process itself.
Challenges in Incident Analysis
Despite its importance, incident analysis can be challenging. Issues such as incomplete data, lack of cooperation from involved parties, and biases in analysis can impede the effectiveness of the process. Additionally, organizations may face challenges in implementing corrective actions, especially if they require significant changes to established procedures or systems.
The Role of Technology in Incident Analysis
As organizations grow and operational complexities increase, the role of technology in incident analysis has become more pronounced. Modern technologies, such as incident management software, data analytics tools, and artificial intelligence, enable organizations to handle incident data more efficiently and accurately.
Utilizing Incident Management Software
Incident management software is a powerful tool that helps organizations automate the recording and management of incident-related data. These systems provide a centralized platform where all incident information can be stored and accessed easily, ensuring that data is consistent and secure. They also help in tracking the status of corrective actions and can alert managers about overdue tasks or unresolved issues.
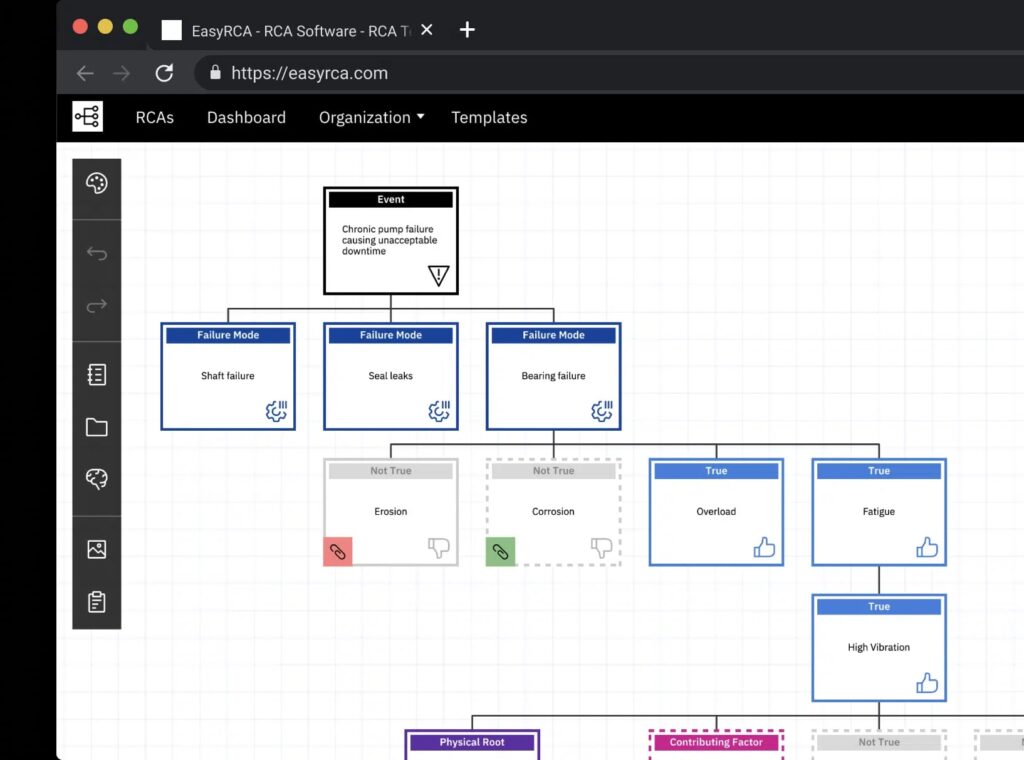
Data Analytics in Incident Analysis
Data analytics plays a crucial role in understanding complex datasets and deriving meaningful insights from them. By applying analytics to incident data, organizations can identify patterns and trends that might not be obvious at first glance. For example, predictive analytics can forecast potential incidents based on historical data, allowing organizations to take preventive measures in advance.
The Impact of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) offers promising enhancements in incident analysis by automating complex processes and providing deeper insights. AI can quickly process large volumes of data to identify anomalies or patterns that human analysts might miss. Furthermore, machine learning algorithms can learn from past incidents to improve their predictive capabilities over time, helping to prevent future occurrences.
Implementing a Successful Incident Analysis Process
Organizations must consider several best practices that ensure the thoroughness and effectiveness of their analyses. This will help with effectively implementing incident analysis processes.
Establishing a Clear Process
The first step is to establish a clear, standardized process for incident analysis that includes defined roles and responsibilities. This process should be documented and accessible to all employees to ensure they understand what needs to be done when an incident occurs.
Training and Awareness
Training employees on the importance of incident analysis and how to conduct it effectively is crucial. This includes training on how to use any relevant technology, understanding the procedures for reporting incidents, and recognizing the signs of potential incidents.
Creating a ‘No-blame’ Culture
To encourage reporting and honest discussion about incidents, it’s vital to foster a no-blame culture. Employees should feel safe to report incidents and near misses without fear of retribution. This environment supports a more accurate and comprehensive incident data collection, which is critical for effective analysis.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Analyzing real-world examples can provide valuable insights into the practical applications and benefits of thorough incident analysis. Here, we can look at case studies from different industries where incident analysis has led to significant improvements in safety and operational efficiency.
Case Study in the Manufacturing Industry
In a manufacturing setting, an incident analysis revealed that recurring equipment failures were due to a lack of regular maintenance and improper use by operators. The organization responded by implementing stricter maintenance schedules and enhanced operator training, which significantly reduced equipment downtime and increased production efficiency.

Source: © Chine Nouvelle/SIPA/Shutterstock
Healthcare Sector Example
In healthcare, a critical incident involving medication errors pointed to flaws in the drug dispensing process. Through detailed analysis, it was found that similar incidents were occurring across multiple departments. The hospital implemented a new bar-coded medication management system, which drastically reduced medication errors and enhanced patient safety.
The Integration of Incident Analysis Across Departments
The effectiveness of incident analysis often hinges on the extent of its integration across various departments within an organization. Different areas of an organization can provide diverse perspectives and insights, which are crucial for comprehensive analysis. This integration not only helps in gathering detailed data but also ensures that the solutions implemented are holistic and encompass all relevant aspects of the organization.
Cross-Departmental Collaboration
To facilitate this integration, organizations should encourage cross-departmental collaboration. This could involve setting up interdisciplinary teams to handle incident analysis, ensuring that each team includes representatives from different departments such as operations, human resources, safety, and IT. Such teams can leverage their varied expertise to dissect the incident from multiple angles, enhancing the quality of the analysis and the effectiveness of the corrective actions.
Sharing Lessons Learned
Another crucial aspect of cross-departmental integration is the sharing of lessons learned from incident analyses. Regularly scheduled review meetings can be useful for discussing recent incidents and sharing feedback across departments. This helps in disseminating knowledge throughout the organization and can prevent the occurrence of similar incidents in different departments.
Conclusion: The Path Forward with Incident Analysis
Incident analysis is more than just a procedural task; it is a strategic tool that can drive significant improvements across all areas of an organization. By learning from past incidents and continually refining processes, organizations can not only prevent similar events in the future but also foster a culture of proactive improvement and safety awareness.
This ongoing commitment to understanding and mitigating risks will not only protect employees but also improve overall operational effectiveness, making incident analysis an indispensable part of modern business practices.
___________
I hope you found this guide to Incident Analysis: Effective Implementation insightful and actionable! Stay tuned for more thought-provoking articles as we continue to share our knowledge. Success is rooted in a thorough understanding and consistent application, and we hope this article was a step in unlocking the full potential of Root Cause Analysis for your organization.
Reliability runs initiatives such as an online learning center focused on the proprietary PROACT® RCA methodology and EasyRCA.com software. For additional resources, visit Reliability Resources.
Recent Posts
How to Improve Your RCA Program: A Practical Guide for Reliability Leaders
The 2026 Reliability Cost Curve: How World-Class Teams Bend It Downward
The Reliability Leader’s 2026 RCA Playbook: A Straightforward Guide to Starting the Year Strong
Why You Never Have Time for Root Cause Analysis (And How World-Class Teams Fix It)
Root Cause Analysis Software
Our RCA software mobilizes your team to complete standardized RCA’s while giving you the enterprise-wide data you need to increase asset performance and keep your team safe.
Root Cause Analysis Training

